代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 #include "sdlqtrgb.h" #include <sdl/SDL.h> #include <QMessageBox> #include <iostream> #pragma comment(lib, "SDL2.lib" ) static int sdl_width = 0 ;static int sdl_height = 0 ;static SDL_Window* sdl_win = nullptr ;static SDL_Renderer* sdl_render = nullptr ;static SDL_Texture* sdl_texture = nullptr ;static unsigned char * rgb = nullptr ;static int pix_size = 4 ;SdlQtRgb::SdlQtRgb (QWidget *parent) : QWidget (parent) { ui.setupUi (this ); sdl_width = ui.label->width (); sdl_height = ui.label->height (); SDL_Init (SDL_INIT_EVERYTHING); sdl_win = SDL_CreateWindowFrom ((void *)ui.label->winId ()); sdl_render = SDL_CreateRenderer (sdl_win, -1 , SDL_RENDERER_ACCELERATED); QImage img1 ("001.jpg" ) ; QImage img2 ("002.jpg" ) ; if (img1.isNull () || img2.isNull ()) { QMessageBox::information (this , "" , "open image failed!" ); } int target_width = 800 ; int target_height = 600 ; float scale1_w = static_cast <float >(target_width) / (img1.width () + img2.width ()); float scale1_h = static_cast <float >(target_height) / std::max (img1.height (), img2.height ()); float scale = std::min (scale1_w, scale1_h); QImage img1_resized = img1.scaled (img1.width () * scale, img1.height () * scale); QImage img2_resized = img2.scaled (img2.width () * scale, img2.height () * scale); int out_w = img1_resized.width () + img2_resized.width (); int out_h = std::max (img1_resized.height (), img2_resized.height ()); sdl_width = out_w; sdl_height = out_h; resize (sdl_width, sdl_height); ui.label->move (0 , 0 ); ui.label->resize (sdl_width, sdl_height); sdl_texture = SDL_CreateTexture (sdl_render, SDL_PIXELFORMAT_ARGB8888, SDL_TEXTUREACCESS_STREAMING, sdl_width, sdl_height ); rgb = new unsigned char [sdl_width * sdl_height * pix_size]; memset (rgb, 0 , sdl_width * sdl_height * pix_size); for (int i = 0 ; i < sdl_height; i++) { int b = i * sdl_width * pix_size; if (i < img1_resized.height ()) memcpy (rgb + b, img1_resized.scanLine (i), img1_resized.width () * pix_size); b += img1_resized.width () * pix_size; if (i < img2_resized.height ()) memcpy (rgb + b, img2_resized.scanLine (i), img2_resized.width () * pix_size); } QImage out (rgb, sdl_width, sdl_height, QImage::Format_ARGB32) ; out.save ("jasonqian_out_resized.jpg" ); startTimer (30 ); } void SdlQtRgb::timerEvent (QTimerEvent *ev) SDL_UpdateTexture (sdl_texture, NULL , rgb, sdl_width * pix_size); SDL_RenderClear (sdl_render); SDL_Rect rect; rect.x = 0 ; rect.y = 0 ; rect.w = sdl_width; rect.h = sdl_height; SDL_RenderCopy (sdl_render, sdl_texture, NULL , &rect); SDL_RenderPresent (sdl_render); } SdlQtRgb::~SdlQtRgb () { SDL_Quit (); }
(一)
1 2 float scale1_w = static_cast <float >(target_width) / (img1.width () + img2.width ());float scale1_h = static_cast <float >(target_height) / std::max (img1.height (), img2.height ());
static_cast 是 C++ 中一种类型转换操作符,用于在编译时执行明确的类型转换。它提供了一种比传统的 C 风格类型转换(如 (type)variable)更安全、可控的类型转换方式。
static_cast 的用途:
基本数据类型之间的转换 :例如,将 int 转换为 float,或将 float 转换为 double。指针类型的转换 :在继承关系中,可以使用 static_cast 将基类的指针转换为派生类的指针,前提是这种转换是安全且合法的。隐式类型转换 :对于可以通过隐式转换的类型(例如从 int 到 float),static_cast 可以显式地执行这种转换。枚举类型和整数之间的转换 :例如,可以将枚举类型转换为整数,反之亦然。
【例子 】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int main () int a = 10 ; double b = static_cast <double >(a); std::cout << b << std::endl; double d = 3.14 ; int i = static_cast <int >(d); std::cout << i << std::endl; }
使用 static_cast 的原因:
类型安全 :static_cast 只允许合理的、明确的类型转换。如果尝试执行不合理的转换,编译器会发出警告或错误。代码可读性 :通过使用 static_cast,程序员和代码审查者可以更清楚地看到何处发生了类型转换,以及转换的目标类型是什么。
【不合理的例子 】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int arr[10 ];int value = static_cast <int >(arr); --- double d = 3.14 ;int * iptr = static_cast <int *>(&d);
(二)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for (int i = 0 ; i < sdl_height; i++){ int b = i * sdl_width * pix_size; if (i < img1_resized.height ()) memcpy (rgb + b, img1_resized.scanLine (i), img1_resized.width () * pix_size); b += img1_resized.width () * pix_size; if (i < img2_resized.height ()) memcpy (rgb + b, img2_resized.scanLine (i), img2_resized.width () * pix_size); }
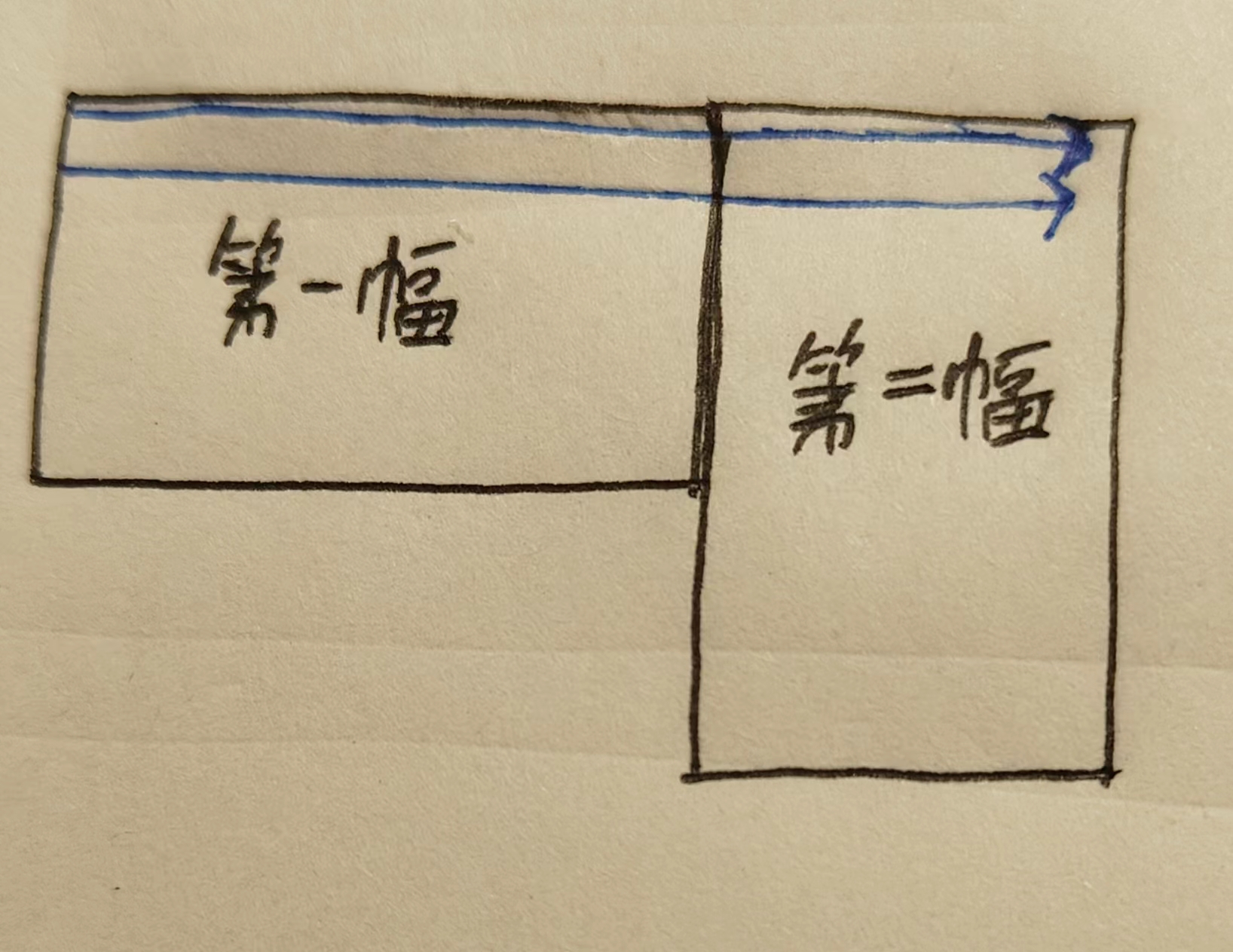
行1 :先复制第一幅图片的第1行,再复制第二幅图片的第1行。
行2 :先复制第一幅图片的第2行,再复制第二幅图片的第2行。
依此类推,直到处理完所有行。
(三)
详情见:使用 SDL 进行 RGB 渲染 。